Nuclear Reactor Construction and Working
Q. What is Nuclear Reactor explain its principle construction and working?
Q. What is the working principle of nuclear power plant?
Q. How does a nuclear reactor work
Q. Explain the principle and working of a nuclear reactor with the help of a labelled diagram
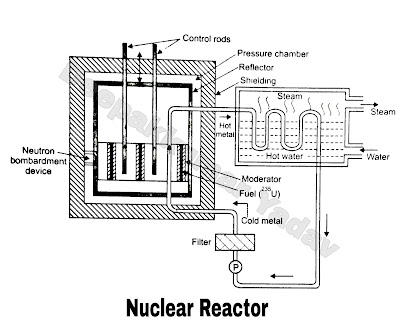
- Nuclear Reactor : It is a heart of nuclear power plant . Controlled chain reaction takes place in nuclear reactor which generates heat. This heat is absorbed by sodium metal which is continuously circulated through the tubes by means of pump. The nuclear reactors mainly consist of fuel (23592U), moderator, control rods, reflector, coolant.
- The reactor core is rectangular in shape, this makes refueling easy and coolant circulation process is also simplified.
- The reflector reflects the free neutron if any. This avoids leakage of free neutrons and thus thermal efficiency increases. The material used for reflector is reactor grade graphite. Reflector also ensures uniform distribution of heat energy.
- Fuel : Fuels used in reactor are 23592U, Fuel is in the shape of rod. These fuel rods are bombarded with slow moving neutrons. The neutrons are bombarded through a special device (neutron bombardment device.
- Moderator : These are in the shape of rod and made up of graphite or heavy water or beryllium. This device moderates or reduces the neutron speed such that probability of fission Increases.
- Note : Neutron at slower speed is required to produce fission.
- Control rods : In a reactor, the chain reaction is to be initiated and it is to be maintained at a steady rate during the reactor operation and under emergency the reactor should be stopped. Chain reaction is controlled by control rods, which absorb the free neutrons as the chain reaction progresses. The control rods are made up of cadmium, boron (alloyed with steel or aluminium). They surround the fuel. Under emergency, another control rods called safety rods are used (not shown in Figure). In case of earthquake, excessive power generation, failure of any control system or any such event leading to safety problems, health hazards, the safety rods are inserted manually or automatically. The safety rods as long as are inserted in the reactor core, the chain reaction stops. When they are completely removed, chain reaction starts, generation of electrical energy starts.
- Shielding : Radiations occur during nuclear fission/ chain reaction which are harmful for living creatures. So proper shielding of the reactor is essential. Concrete is used as a shielding material.
- Heat exchanger : The heat energy released in a reactor core is absorbed by the coolant (sodium metal), it becomes hot (hot metal) and it is continuously circulated through heat exchanger. The hot metal gives away heat to water, water boils and steam is produced at high pressure. This steam is passed on to the steam turbine through a valve.
- The coolant becomes cold metal after giving away heat in heat exchanger. It is circulated to reactor again through a pump after filtration. During filtration the impurities in coolant If any are removed.
- Turbine : The steam turbine rotates when steam Impinges on it. It gives mechanical output to alternator and alternator generates the electricity. The steam after doing useful work is passed on to the condenser.
- Condenser : The condenser condenses the steam with the help of water taken from water treatment chamber and cooling tower. The condensed steam is further heated in feed water heater.
- The heating is done by tapping some steam from the turbine (bleeding of the turbine).
- Feed water heater :Feed water heater is used to increase the thermal efficiency of a plant. Some part of steam from steam turbine is used to heat the water (bleeding of turbine). This heated water is now passed to heat exchanger with the help of pump. Water treatment chamber is used to remove impurities from water.
- Reflector : This completely surrounds the reactor core within the thermal shielding arrangement and helps to bounce the escaping neutrons back into the core. This conserves the nuclear fuel as the low speed neutrons thus returned are useful in continuing the chain reaction. It is required to provide some method of cooling the reflector as it gets heated due to collision of neutrons with its atoms.
- Coolant : A coolant transfers heat produced inside the reactor to a heat exchanger for further utilization In power generation. When water is used as a coolant it takes up heat and gets converted into steam in the reactor which is directly used in the turbine Coolant flows through and around the reactor core. The coolants commonly used are gas (carbon dioxide, air, hydrogen, helium etc.), water, heavy water, liguid metals (sodium of sodium-potassium) and some organic liquids.
- Reactor Vessel : This encloses the reactor core, reflector and shield. It is a strong walled container which also provides the entrance and exit passages for directing the flow of coolant. The reactor vessel has to withstand high pressures. The holes at the top of the vessel are provided to insert the control rods. The reactor core (fuel and modulator assembly) is generally placed at the bottom of the vessel